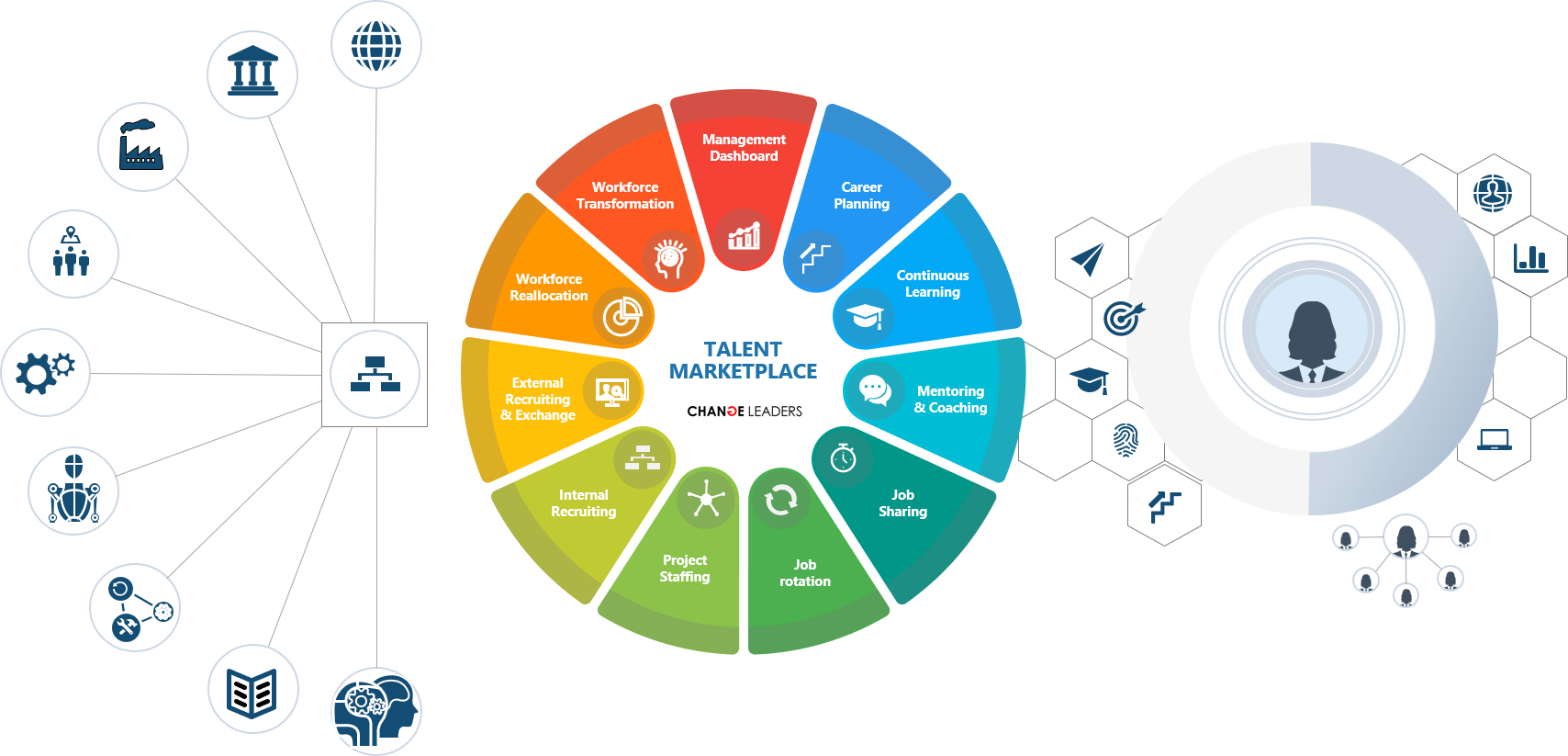
ENTERPRISE TALENT MARKETPLACE
The way we define work will change fundamentally: We will focus on assignments and tasks, rather than jobs and roles, and we will assemble the most appropriate and engaged talent to complete those assignments and tasks. Enterprise talent marketplaces will enable organizational and talent agility. They will connect the assignments and tasks required to execute a specific business strategy with the right people. Individuals will work on their professional reputation and visibility in internal and external networks to shape their careers on their own terms.
We help to establish a transparent, open and adaptive marketplace
for supply, demand and development of hard & soft skills
to increase employability, productivity and engagement.
TRENDS & DRIVERS
- Demographic development
- Multi-generational workforce with different expectations
- Changing skill requirements due to digitalization, automation and workforce augmentation (interaction of humans and machines through artificial intelligence)
- New forms of organization and work in the context of New Work
- Multiple/flexible employment structures
- Innovative Talent Solutions
BASIC PRINCIPLES
- Democratization and individualization of professional development
- Transparent: availability of and access to task-based skill requirements and individual skill profiles
- Adaptive: flexibly adaptable to changing skill requirements and offerings
- Open: cross-organizational and possible link to career site and external job boards
Download Whitepaper:
Talent Marketplace
KEY CHALLENGES
- Development of a new career mindset
- Development of a new HR & leadership mindset (from learning provider to learning enabler and designer of learning environments)
- Changing roles of HR, managers and employees
- Regulation of „market processes“, e.g. recruiting, job evaluation, assignment and skill-based pay, employee appraisal, feedback
- Co-determination/works agreements, labor law and data protection
TALENT MARKETPLACE
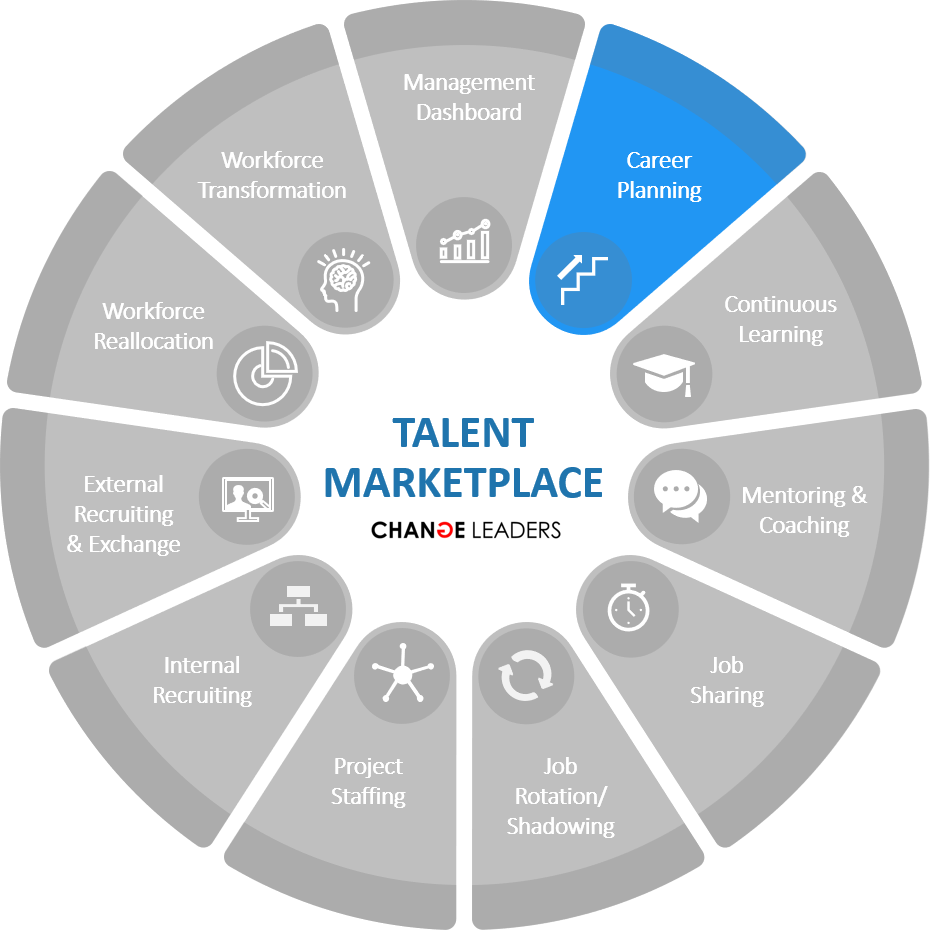
CAREER PLANNING
- Experienced experts and managers offer their know-how and experience as mentors or coaches.
- Employees and managers seek advice from experienced experts and colleagues.
- By matching respective skills profiles, mentees and mentors, coachees and coaches are brought together.
- My new job is a real challenge. Is there someone with the right skills to provide me some coaching?
- The conflict situation in my team is very demanding. Who could give me some tips and support me with his or her experience?
- I am looking for a mentor to guide me in my professional development.
- I am a real expert in my field and would like to pass on my know-how to others. Is there someone looking for a coach with my skills?
- Retention and dissemination of internally available knowledge and know-how.
- Promoting collegial consultation and networking.
- Developing solutions for concrete questions and problems of everyday professional life.
- Support in taking on managerial tasks.
- Support in the development of solutions for concrete questions and problems of everyday professional life.
- Advice on decisions regarding career development.
- Possibility to seek neutral, independent, collegial and trustworthy support, even outside their own organisational unit.
- Opportunity to pass on one‘s knowledge and experience to interested employees and managers as a mentor or coach.
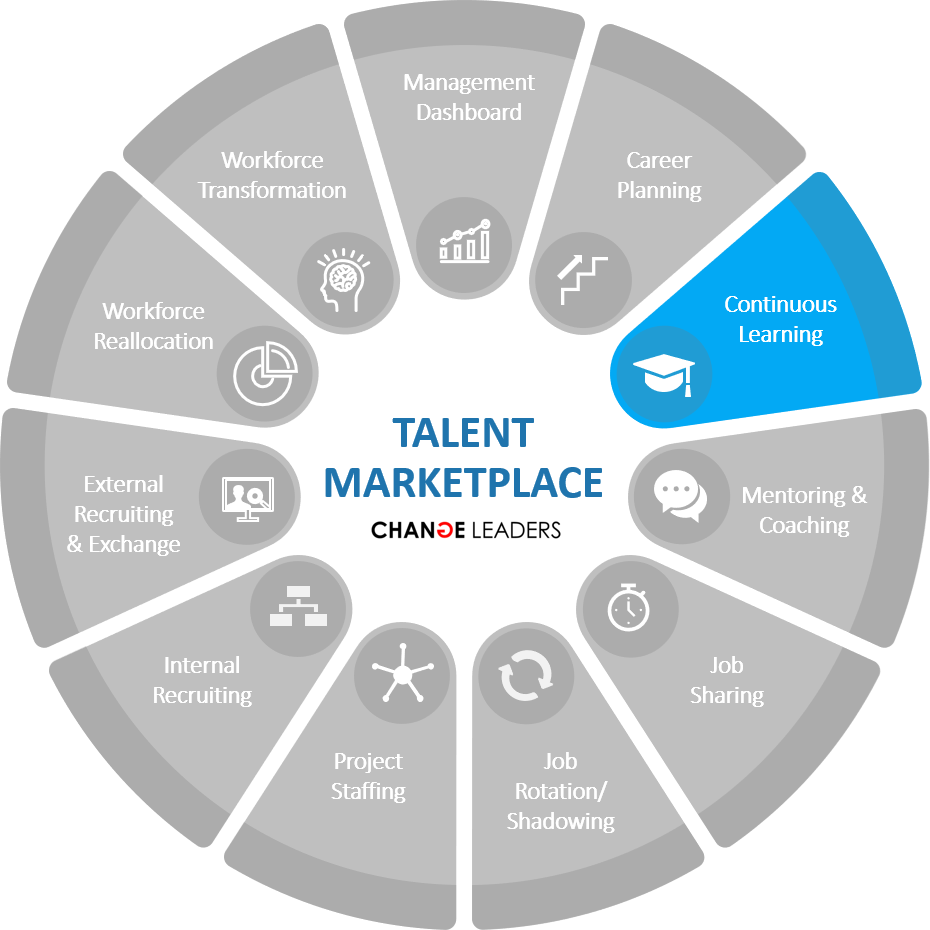
CONTINUOUS LEARNING
- Employees (including managers) regularly find out about the hottest skills and latest learning opportunities in their field or regarding specific topics on a special learning platform.
- Various learning opportunities: digital and integrated into the workflow: macro, micro, academy & experiential learning.
- Example macro learning: structured content to develop new hard and soft skills.
- Example micro learning: unstructured content for rapid ad-hoc learning of experts.
- Fast growing market with specialised providers of learning management systems and content platforms.
- I am currently working on an assignment and would like to refresh my methodological skills.
- Which learning opportunities help me to get prepared for future requirements in my job?
- I would like to become a sought-after expert in my professional field. What would be the learning paths to continuously develop my skills?
- I would like to be able to perform tasks in a related field and become more flexibly deployable. How can I acquire the additional knowledge?
- I would like to change departments. How can I get ready for my new job?
- Developing learning agility and ensuring future employability of staff.
- Securing and developing the core competences and organizational capabilities that are critical for the future success of the company and its business units.
- Broadening the skills base and increasing the flexibility of employees.
- Promotion of the competence career as an alternative to a hierarchical career.
- Increasing employees‘ personal responsibility and motivation learn.
- Possibility to develop according to own personal interests and within own responsibility.
- Broad and up-to-date learning offer to shape hard and soft skills.
- Opportunity to prepare systematically for new tasks.
- Unlimited access in terms of time and space to interesting learning content, even beyond one’s own professional horizon.
- Allowing for more flexible deployment opportunities.
- Securing own employability by acquiring the skills required in the future.
MENTORING & COACHING
- Experienced experts and managers offer their know-how and experience as mentors or coaches.
- Employees and managers seek advice from experienced experts and colleagues.
- By matching respective skills profiles, mentees and mentors,
coachees and coaches are brought together.
- My new job is a real challenge. Is there someone with the right skills to provide me some coaching?
- The conflict situation in my team is very demanding. Who could give me some tips and support me with his or her experience?
- I am looking for a mentor to guide me in my professional development.
- I am a real expert in my field and would like to pass on my know-how to others. Is there someone looking for a coach with my skills?
- Retention and dissemination of internally available knowledge and know-how.
- Promoting collegial consultation and networking.
- Developing solutions for concrete questions and problems of everyday professional life.
- Support in taking on managerial tasks.
- Support in the development of solutions for concrete questions and problems of everyday professional life.
- Advice on decisions regarding career development.
- Possibility to seek neutral, independent, collegial and trustworthy support, even outside their own organisational unit.
- Opportunity to pass on one‘s knowledge and experience to interested employees and managers as a mentor or coach.
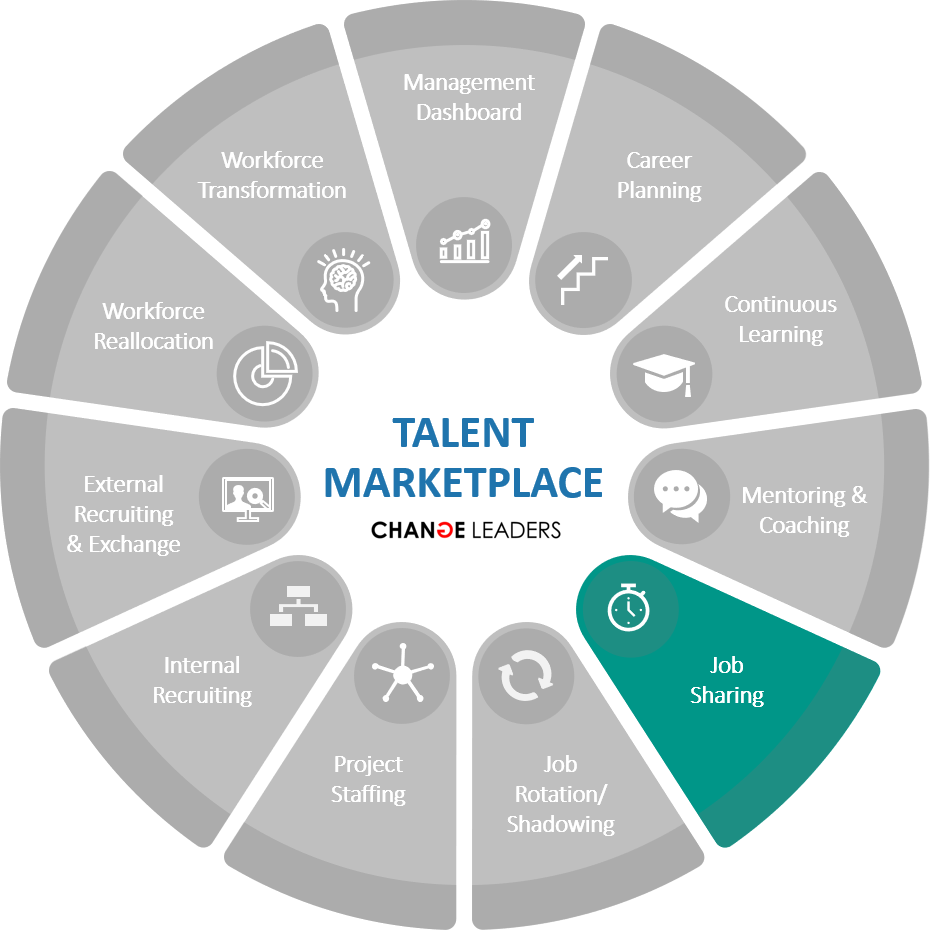
JOB SHARING
- Employees and managers, for a variety reasons, are looking for ways to reduce their working time. They don’t want to give up their job altogether or switch to a lower-quality job. They are looking for a part-time job that satisfies them and that suits their skills.
- The Job Sharing platform offers employees and managers the opportunity to find other people with similar needs and to check the fit for the respective job profile via a skills match.
- I would like to take more care of my children. Is there anyone in a similar situation who would like to share a job?
- My parents need my support in the next couple of years. Is there a job that suits my skills and that I can share with someone else?
- I am planning a flexible transition into retirement and would like to share my job with someone else. Maybe there is even a part-time job outside my organisational unit that would mesh with my skills?
- I would like to take a step back for health reasons and am looking for a part-time job.
- Maintaining/increasing the motivation of specific employee groups.
- Retaining knowledge and avoiding unwanted turnover.
- Contributing to employee health and wellbeing.
- Strengthening employee value proposition and engagement.
- Strengthening of external employer brand.
- Contributing to society as a whole.
- Possibility to reduce working hours at the same skill and job level.
- Better ability to balance work with family and health matters.
- Opportunity of a flexible exit from working life.
JOB ROTATION & SHADOWING
- Employees and managers are seeking for variety and change. They are interested in similar or different jobs in other parts of the organization.
- The desire for variety can be temporary or triggered by a general motivation for change.
- The Talent Marketplace offers the possibility to search for job rotation and job shadowing opportunities across the organization, based on respective tasks and skills requirements.
- I would like to get to know the team with whom I work together on a daily basis. Maybe in their location is someone with the same or a simliar job that I do and who might be interested in a temporary job rotation?
- I would like to develop further in my field and shadow an expert for some time.
- I am interested in a job in another department and would like to find out more about it. Is there an opportunity to shadow someone or a team?
- Promoting internal mobility across businesses and geographies.
- Broadening the experience level of staff.
- Enabling organization-wide networking.
- Facilitating the flexible deployment of employees across the organization.
- Supporting qualified change and development decisions by staff.
- Increasing the motivation and retention of employees who are looking for a change.
- A chance to add variety to daily work routine.
- Opportunity to get to know other jobs, teams and locations.
- Opportunity to broaden one’s experience, to shadow and learn from others.
- Opportunity to validate own interest in career change and to improve the underlying decision basis.
PROJECT STAFFING
- Departments search the Talent Marketplace for suitable project managers for strategic initiatives.
- Departments advertise task- and skill-based project manager positions on the Talent Marketplace.
- Program and project managers are looking for employees with the right skill profiles for their projects.
- Program and project managers advertise project assignments with defined skill profiles.
- Managers and employees search for project assignments that match their skill profile.
- In my previous marketing job I worked with SPSS and used multivariate analyses to identify different market segments. Maybe my experience could be of good use in the new sales project?
- I am looking for a project manager for an important strategic initiative, who understands well our vision, doesn’t lose sight of the big picture and can manage the sub-projects in an agile manner with OKR methodology.
- I would like to staff the individual topics and sub-projects of my workstream with specialists in the respective subject areas.
- Increasing organization-wide transparency of projects, respective skill requirements and staffing decisions.
- Broadening the search space for project appointments.
- Breaking down organizational barriers and reducing recruiting bias in project staffing.
- Improving project staffing and enriching and updating often limited employee data in HR systems.
- Increasing employee engagement.
- Promoting internal mobility.
- Organization-wide transparency of projects, skill requirements and project staffing.
- Improved accessibility of project assignments.
- Improved possibility to get information about the professional background and skills of members of a project team.
- Improved possibility to compare the own skill profile with the required skills in a project.
INTERNAL RECRUITING
- Departments and/or recruiters post vacancies with task and skill-based job profiles.
- Employees (including managers) inform themselves about the skill requirements of open positions (also beyond their organisational unit).
- By matching the employee’s skills profile with the job profile (skill matching), the department offering the job as well as interested candidates get specific indications about the degree of fit (gap analysis).
- How can we recruit faster across silos and do a better job in staffing open positions?
- What digital skills must an expert have in the field of process management?
- Do we have employees somewhere in the organization who gained in previous jobs experience in process mining, process automation & workflow management?
- What should we look for when filling a new job in our field work? What skills do our best field staff have?
- Which jobs are currently available? Which jobs could fit my skill profile?
- Increasing organization-wide transparency of open positions, skill requirements and staffing decisions.
- Broadening the search space for stafing decisions.
- Breaking down organizational barriers and reducing recruiting bias in staffing decisions.
- Improving staffing decisions and enriching and updating often limited employee data in HR systems.
- Increasing employee engagement.
- Promoting internal mobility.
- Organization-wide transparency of open positions, skill requirements and staffing decisions.
- Improved access to the internal job market.
- Improved possibility of getting information about the professional background and skills of the members of a team.
- Improved possibility to compare the own skill profile with the required skills of a job.
EXTERNAL RECRUITING & EXCHANGE
- Integration/coordination of internal and external talent marketplaces.
- Recruiters post job openings along with task- and skill-based job profiles on their own career site and on external job boards.
- Interested external candidates find out about the vacancies, enter their skills profile to understand the skills fit with the open position, to then decide whether or not to apply.
- If necessary, the internal talent marketplace can be extended to ecosystem/ value chain partners, to develop and post (temporary) staff exchanges.
- What skill profile do I need to have to apply for the job?
- What skill profiles do we need to look for? For example: What are the skill profiles of digital learning experts in the market? Or: What skills must a digital process management expert have?
- In which sectors and positions do we most likely find the skill profiles we are looking for?
- With which cooperation partners or companies in our business ecosystem that have jobs with similar skill profiles could we develop joint offers for a development or demand-driven exchange of personnel?
- Improving decision making when staffing open positions with external candidates.
- Faster and better recruitment and staffing.
- Establishment of an inter-company talent pool with cooperation partners and other companies.
- Qualified skills-based networking with external talent and buildup of an external talent pool.
- Systematic and planful integration of internal and external talent marketplaces.
- Transparency about jobs and skills profiles that are advertised externally.
- Transparency about jobs advertised on the inter-company market.
- Broadening development opportunities by adding an inter-company exchange cooperation.
WORKFORCE REALLOCATION
- In addition to the pandemic, technological developments and in particluar digitalisation are driving new and often different staff requirements in the various organisational units.
- Matching, for example, skills required in the growing organisational unit A with existing employee skills in organisational unit B affected by automation provides a good basis of information to support long-term personnel development and transfers.
- On the basis of skills profiles, temporary and seasonal shifts in demand can be met with respective staff re-deployment.
- If required, outplacement measures can be supported.
- How can we respond to the shifts in demand triggered by the Corona pandemic through internal staff transfers?
- How can we respond to the changes in the information and buying behaviour of customers and the resulting consequences for sales?
- How can we proactively prepare the workforce segments affected by automation and robotics by developing skills required in other jobs?
- How can we support employees with skill profiles who, due to the business situation, can no longer find internal employment opportunities, in preparing them for the external market?
- Facilitating the flexible allocation of staff capacity e.g., to compensate for short-term fluctuation in demand and secure maximum value creation (workforce reallocation/transfer management)
- Identifying early on jobs and skill profiles at risk and developing future-proof skills (reskilling, upskilling).
- Supporting cross-business and geographical mobility.
- Avoiding reduction in force measures.
- Positive influence on the employer brand.
- Securing employment with current employer.
- Possibility to contribute with existing skills in another unit or at another location.
WORKFORCE TRANSFORMATION
- Routine tasks will get increasingly automated, as robots and AI are entering the world of work. Depending on the job, the share of activities that can be automated can vary greatly. Some jobs will disappear, new jobs will emerge
- Cooperation between men and machines will become a critical success factor and productivity driver.
- The systematic identification of essential future skills and their development in large parts of the workforce is at the core of digital transformation programs and the foundation of its success.
- How can we ensure the digital literacy of our workforce, and how do we know where we stand in its development?
- What are the mission-critical future skills in which domains?
- How do we create positive experiences and a we-can-do-it-atmosphere with respect to digitalization?
- How can we support cross-divisional collaboration in agile ways of working?
- How can we provide, across the enterprise, insights into new ways of performing work, e.g. through project work, on-the-job learning formats and communities of practice?
- The success of digital transformation programs is less a question of technology than a question of employee attitude and skills.
- All learning opportunities, off-the-job and on-the-job, are made transparent and available to all employees on a digital marketplace.
- Learning impact gets measurable and can be systematically tracked and incentivized.
- Managers are supported in their special role as as ‚learning enablers‘ and coaches.
- Digital talent gets attracted and retained.
- Digitalization is perceived more as an opportunity and less as a threat.
- AI and robotics are experienced positively as supporting tools.
- As an employee, I know where I stand and how I can increase my employability.
- Access to a variety of learning and development opportunities.
- If a job is no longer available, there is support in finding internal and external alternatives.
MANAGEMENT DASHBOARD
- The dashboard provides real-time insight into all aspects of the talent marketplace at enterprise and business unit-level.
- Support is provided in particular for learning and development, knowledge management, recruiting and staffing, mobility, flexible use of resources and the development of an agile mindset.
- KPIs link the various HR measures to business data to control for the added value.
- How does the half-life of skills evolve in different departments?
- Which jobs are threatened in the future and how can we take timely measures?
- Did the upskilling measures in unit A have the desired impact?
- Should we meet the high demand for skills in the field of artificial intelligence and robotics by using external specialists?
- How can work be fractionated so that we can continue to make good use of the skills we have got?
- Securing future skills and competences at organization and staff level.
- Control and flexibilization of different workforce segments in a transparent and open market where employees take on responsibility for their development.
- Real-time people analytics and workforce management: In times of VUCA, digitalization and agile management, the capability to respond real time is critical to success. In this context strategic workforce planning is for the bin.
- Skill-based job design by managers (job design).
- Skill-based recruiting and staffing decisions by managers.
- Access to various targeted and up-to-date learning opportunities.
Innovative Consulting & Digital Solutions